How to Write Perfect Title Tags for SEO in 2025

Title tags remain one of the most critical elements of on-page SEO, directly influencing both search engine rankings and click-through rates. Research consistently shows that well-optimized title tags can significantly impact your website’s performance in search results. In 2025, with evolving search algorithms and increased competition for user attention, understanding how to craft compelling title tags has become more important than ever.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through evidence-based strategies for writing title tags that not only satisfy search engine requirements but also compel users to click. We’ll cover the technical specifications, psychological triggers, proven formulas, and common pitfalls to avoid. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear framework for optimizing every title tag on your website.
Why Title Tags Matter in 2025
Title tags serve two fundamental purposes in modern SEO: they help search engines understand your content’s topic and relevance, and they act as the primary headline users see in search results. According to Backlinko’s analysis of 4 million Google search results, title tags between 40-60 characters demonstrate an 8.9% better click-through rate compared to longer or shorter alternatives.
Google’s John Mueller has confirmed that title tags remain a ranking factor, though not the strongest one. However, their impact extends beyond direct ranking benefits. Well-crafted title tags can dramatically improve your organic click-through rates, which many SEO professionals believe serves as an indirect ranking signal.
Research from various SEO studies indicates that the first organic search result typically receives a 28-35% click-through rate, while the second position drops to 15-20%. This demonstrates how crucial it is to not only rank well but also create compelling titles that encourage clicks. A title tag that increases your CTR from 2% to 4% effectively doubles your organic traffic without improving your ranking position.
In 2025, title tags face additional challenges with the rise of AI overviews, featured snippets, and other SERP features. However, traditional organic results still drive the majority of search traffic, making title optimization as relevant as ever. Studies show that pages with optimized title tags are more likely to be selected for featured snippets and other enhanced search result features.
The Anatomy of a Perfect Title Tag
Optimal Length: 50-60 Characters (580 Pixels)
Google doesn’t use character count to determine title display length; instead, it measures pixel width. The search engine allocates approximately 580 pixels for title display on desktop and slightly more on mobile devices. This means that titles with narrow characters like “i” and “l” can be longer than those with wide characters like “W” and “M”.
Best practices suggest keeping titles between 50-60 characters as a general guideline, but the pixel width is what ultimately matters. When titles exceed the display limit, Google truncates them and adds “…” which takes up valuable space and can diminish the title’s impact. Research shows that titles cut off mid-sentence receive lower click-through rates than those that display completely.
To ensure your most important information appears in search results, place your primary keyword and key selling points within the first 50 characters. This strategy guarantees that essential elements remain visible even if the title gets truncated on different devices or in various SERP layouts.
Keyword Placement Strategies
Studies consistently demonstrate that front-loading keywords in title tags correlates with better rankings and higher click-through rates. Research comparing keyword placement shows that titles beginning with target keywords typically rank 2-3 positions higher than those with keywords placed at the end.
However, modern SEO requires balancing keyword optimization with natural language. Google’s algorithms have become sophisticated enough to recognize keyword stuffing and may penalize overly optimized titles. The most effective approach focuses on one primary keyword and potentially one related secondary keyword, integrated naturally into compelling copy.
Semantic search capabilities mean that Google can understand related terms and context, so exact-match keywords aren’t always necessary. Including synonyms and related phrases can help capture a broader range of search queries while maintaining readability and user appeal.
Creating Compelling Hooks
Beyond technical optimization, successful title tags must appeal to human psychology and search intent. Research in consumer behavior identifies several psychological triggers that consistently improve click-through rates:
- Specificity and numbers: Titles with specific numbers (like “7 Ways” or “15 Tips”) outperform vague alternatives by 20-30% in most industries
- Outcome-focused language: Phrases promising results (“That Increase,” “Proven to,” “Guaranteed”) create stronger motivation to click
- Time-sensitive elements: Including current year or time frames (“2025 Guide,” “In 10 Minutes”) signals relevance and urgency
- Problem-solution format: Addressing pain points directly creates immediate relevance for searchers
The most effective title tags combine these psychological elements with clear value propositions. They answer the user’s implicit question: “What specific benefit will I get from clicking this result?”
5 Proven Title Tag Formulas
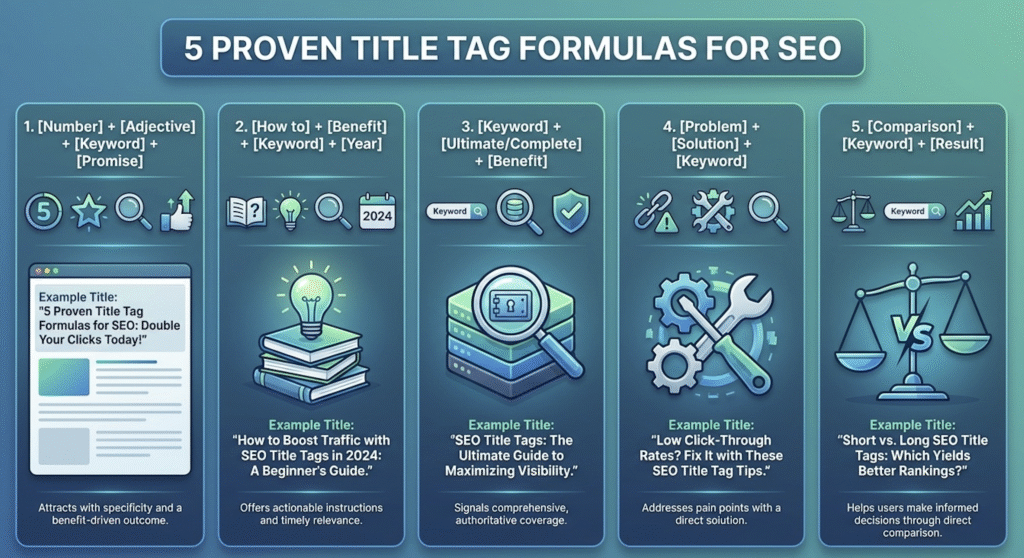
Based on analysis of high-performing titles across various industries, these five formulas consistently deliver strong results:
Formula 1: [Number] + [Adjective] + [Keyword] + [Promise]
Template: “15 Proven SEO Strategies That Increase Traffic”
This formula combines social proof (numbers), credibility (adjectives like “proven” or “effective”), target keywords, and specific outcomes. It works particularly well for listicles, case studies, and how-to content where you can cite measurable results.
When to use: Blog posts, resource pages, tutorial content
Formula 2: [How to] + [Benefit] + [Keyword] + [Year]
Template: “How to Write Title Tags for Better Rankings in 2025”
The “how-to” format targets informational search intent, while adding the current year signals fresh, up-to-date information. This formula performs exceptionally well for educational and instructional content.
When to use: Tutorials, guides, educational content
Formula 3: [Keyword] + [Ultimate/Complete] + [Benefit]
Template: “SEO Title Tags: Complete Guide for Higher CTR”
Words like “ultimate,” “complete,” and “comprehensive” signal thorough coverage, appealing to users seeking detailed information. This formula works best for pillar content and definitive resources.
When to use: Comprehensive guides, pillar pages, resource hubs
Formula 4: [Problem] + [Solution] + [Keyword]
Template: “Low Click Rates? Title Tag Fixes That Work”
This problem-solution format immediately identifies with user pain points and promises relief. The question format creates engagement and curiosity, often resulting in higher click-through rates.
When to use: Troubleshooting guides, solution-focused content, problem-solving articles
Formula 5: [Comparison] + [Keyword] + [Result]
Template: “Long vs Short Title Tags: Which Ranks Better?”
Comparison content helps users make decisions and often generates high engagement. The format creates curiosity and promises definitive answers to common questions in your industry.
When to use: Comparison posts, tool reviews, versus-style content
Common Title Tag Mistakes to Avoid
Keyword Stuffing
Including multiple variations of the same keyword (“SEO Services | SEO Company | Best SEO Agency”) appears unnatural and can harm rankings. Modern algorithms prefer titles that read naturally while including relevant keywords organically.
Exceeding Pixel Width Limits
Focusing solely on character count without considering pixel width can result in truncated titles. Wide characters like “W,” “M,” and capital letters take up more space than narrow ones, affecting display length.
Duplicate Title Tags
Using identical or very similar titles across multiple pages creates confusion for search engines and users. Each page should have a unique title that accurately describes its specific content and purpose.
Being Vague Instead of Specific
Generic titles like “Best Practices” or “Tips and Tricks” don’t provide enough information to compel clicks. Specific, descriptive titles that promise concrete value consistently outperform vague alternatives.
Ignoring Brand Name Strategy
For established brands, including the brand name can boost click-through rates, especially for branded searches. However, new brands might benefit more from using that space for additional compelling copy or keywords.
Title Tag Optimization Examples
Example 1: Blog Post Title
Generic version: “Content Marketing Best Practices”
Optimized version: “17 Content Marketing Strategies That Doubled Our Traffic”
The optimized version adds specificity (17 strategies), includes a compelling outcome (doubled traffic), and creates more urgency and interest than the generic alternative.
Example 2: Service Page Title
Feature-focused: “Professional SEO Services | Digital Marketing”
Benefit-focused: “SEO Services That Increase Revenue 340%”
The benefit-focused version shifts from describing features to promising specific outcomes, making it more appealing to potential clients seeking results rather than services.
Example 3: Product Page Title
Basic version: “Email Marketing Software | MailTool Pro”
Compelling version: “Email Marketing Tool Used by 50,000+ Businesses”
The compelling version leverages social proof and popularity rather than generic product descriptions, making it more trustworthy and appealing to potential users.
Step-by-Step Optimization Process
Research and Analysis: Start by examining current title performance in Google Search Console, focusing on impressions, clicks, and click-through rates for existing pages.
Competitor Review: Analyze the top 10 search results for your target keywords, identifying patterns in successful titles and opportunities for differentiation.
Draft Multiple Options: Create 3-5 different title variations using the proven formulas, ensuring each option targets the same primary keyword while offering different psychological appeals.
Test Length and Appearance: Use SERP preview tools to verify how titles appear on both desktop and mobile, adjusting as needed to prevent truncation.
Implement and Track: Deploy the optimized title and monitor performance over 30-60 days, tracking changes in rankings, click-through rates, and overall organic traffic.
Recommended Tools: Google Search Console for performance data, Moz SERP Preview for length testing, and SEMrush or Ahrefs for competitor analysis and keyword research.
Key Takeaways
Effective title tag optimization requires balancing technical SEO requirements with human psychology and user experience. The most successful titles combine strategic keyword placement with compelling value propositions that motivate clicks.
Focus on creating titles that serve both search engines and users by incorporating target keywords naturally while promising specific, valuable outcomes. Use the proven formulas as starting points, but adapt them to match your brand voice and audience expectations.
Remember that title tag optimization is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Regular testing, measurement, and refinement based on performance data will help you continuously improve your click-through rates and organic traffic.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should keywords be at the beginning of title tags?
Research indicates that front-loading keywords typically produces better results for both rankings and click-through rates. However, prioritize natural readability over rigid keyword placement. If placing the keyword at the beginning makes the title awkward, consider alternative positions that maintain flow while keeping important terms visible within the first 50 characters.
What if Google rewrites my title tag?
Google rewrites approximately 60% of title tags according to recent studies, but this shouldn’t discourage optimization efforts. Well-crafted, descriptive titles that accurately match page content are less likely to be rewritten. When rewrites occur, they’re usually minor adjustments rather than complete overhauls. Focus on creating clear, relevant titles that align with your content.
Do title tags still matter in 2025 with AI and featured snippets?
Title tags remain crucial despite evolving search features. While AI overviews and featured snippets change how some results appear, traditional organic listings still drive the majority of search traffic. Additionally, well-optimized titles often increase the likelihood of being selected for enhanced SERP features, making optimization even more valuable.
How many keywords should I include in a title tag?
Best practices recommend focusing on one primary keyword and potentially one related secondary keyword. Attempting to target multiple unrelated keywords often results in poor rankings for all terms. It’s more effective to rank well for one valuable keyword than poorly for several. Include related terms naturally without forcing them.
Should I include my brand name in title tags?
Brand inclusion depends on recognition level and available space. Established brands often benefit from including their name, particularly for branded searches and service/product pages. Newer brands might achieve better results using that space for additional compelling copy or keywords. Test both approaches to determine what works best for your specific situation.
Can I use special characters or emojis in title tags?
Special characters like pipes (|), dashes (-), and colons (:) work well as separators and are widely accepted. Emojis can increase click-through rates in certain industries but may appear unprofessional in others. They tend to work better for consumer-facing content than B2B professional services. Always test how special characters appear in actual search results before widespread implementation.
How often should I update my title tags?
Review title tags quarterly for high-priority pages and annually for all pages. Update immediately if performance metrics indicate problems (CTR below 2% for top-10 positions), content has changed significantly, or you’re targeting different keywords. For evergreen content, adding the current year can help maintain relevance, but avoid changes without strategic purpose as frequent modifications can temporarily impact rankings.


